Catalyzing Finanical Inclusion through National Strategies
CGAP’s Focus Note outlines roles that Governments can play in promoting the development of inclusive financial ecosystems, including through rules, infrastructure and transaction volumes. National Financial Inclusion Strategies provide an effective framework for the successful implementation of these roles.
National Financial Inclusion Strategies, together with clear mandates, can accelerate progress towards financial inclusion. Regulators with a financial inclusion strategy are likely to have more financial inclusion topics under their purview and more resources and staff dedicated to working on these matters. This can more effectively catalyze the private sector response that is needed to dramatically raise financial inclusion. For example reforms that strengthen financial infrastructure underpin the introduction of low cost and lower risk products and delivery models that are critical to expanded financial inclusion.
However, increased access to finance does not necessarily imply increased usage of financial services. Financial inclusion strategies, including targets and proposed reforms, should be based on ‘demand side’ data on the type and design of financial services that households and firms need, and the ways in which they can access and use those services. World Bank enterprise surveys, household surveys, and the new Findex survey (a global financial inclusion demand-side data project in 150 countries), can be used to provide this critical information.
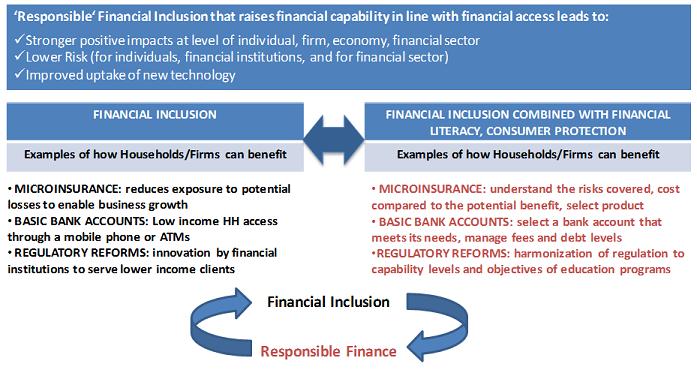
‘Responsible’ Financial Inclusion can lead to stronger positive impacts and lower risks for individuals and financial institutions as well as the financial sector and the economy a whole. Where new consumers are not well protected, or able to take informed decisions about new financial services, or where new products or institutions are not well monitored, then the impacts of financial inclusion can be limited or even negated. This was clearly illustrated by the sub-prime housing loan crisis in the US, the recent payments protection insurance ‘scandal’ in the UK, and microcredit repayment crises in India, Morocco, and elsewhere.
National strategies that focus on responsible financial inclusion, as opposed to simply access to finance, can lead to significantly greater benefits for households and service providers alike. Therefore financial inclusion strategies need to include financial capability and consumer protection as central themes. The World Bank draft Guidelines for Consumer Financial Protection and the OECD Principles and Good Practices for Financial Awareness and Education are key resources.
The Financial Inclusion Practice of the World Bank is committed to supporting governments and regulators in developing and implementing responsible financial inclusion commitments and strategies,through its network of over 170 specialists working with over 60 countries worldwide. We will work closely in fulfilling this commitment to countries with partners such as IFC, CGAP, OECD, UNCDF, the Alliance for Financial Inclusion, regional development banks, and leading donors.


Add new comment