Mobile Money Adopters – Who Are They And What Can They Teach Us?
Knowing more about people who have adopted mobile money (MM) should provide insights into the type of individual that is most likely to adopt MM in the future. And that should help in the design of targeted below the line marketing campaigns; ultimately increasing the take up and usage of MM at a faster rate.
Admittedly it’s almost certainly not as easy as this, but we believe it’s worth exploring further.
We therefore commissioned a data analytics firm, Real Impact, to test this hypothesis. This analysis is part of a broader CGAP series exploring the use of data to advance uptake and usage of MM, particularly amongst poor people. Subsequent research will (i) examine the link between voice and MM corridors, (ii) analyze the spread of MM around the most active MM user of a deployment, and (iii) present the results from marketing campaigns that test the insights from this data analysis.
Today we are releasing the first phase of the analysis - available here. What can voice, SMS, MM, recharge and other data tell us about the characteristics of adopters? These results are the outcome of innovative analytics and data mining techniques - processing a data set of 7 billion transactions performed by more than 10 million mobile phone users across three countries over a seven month period.
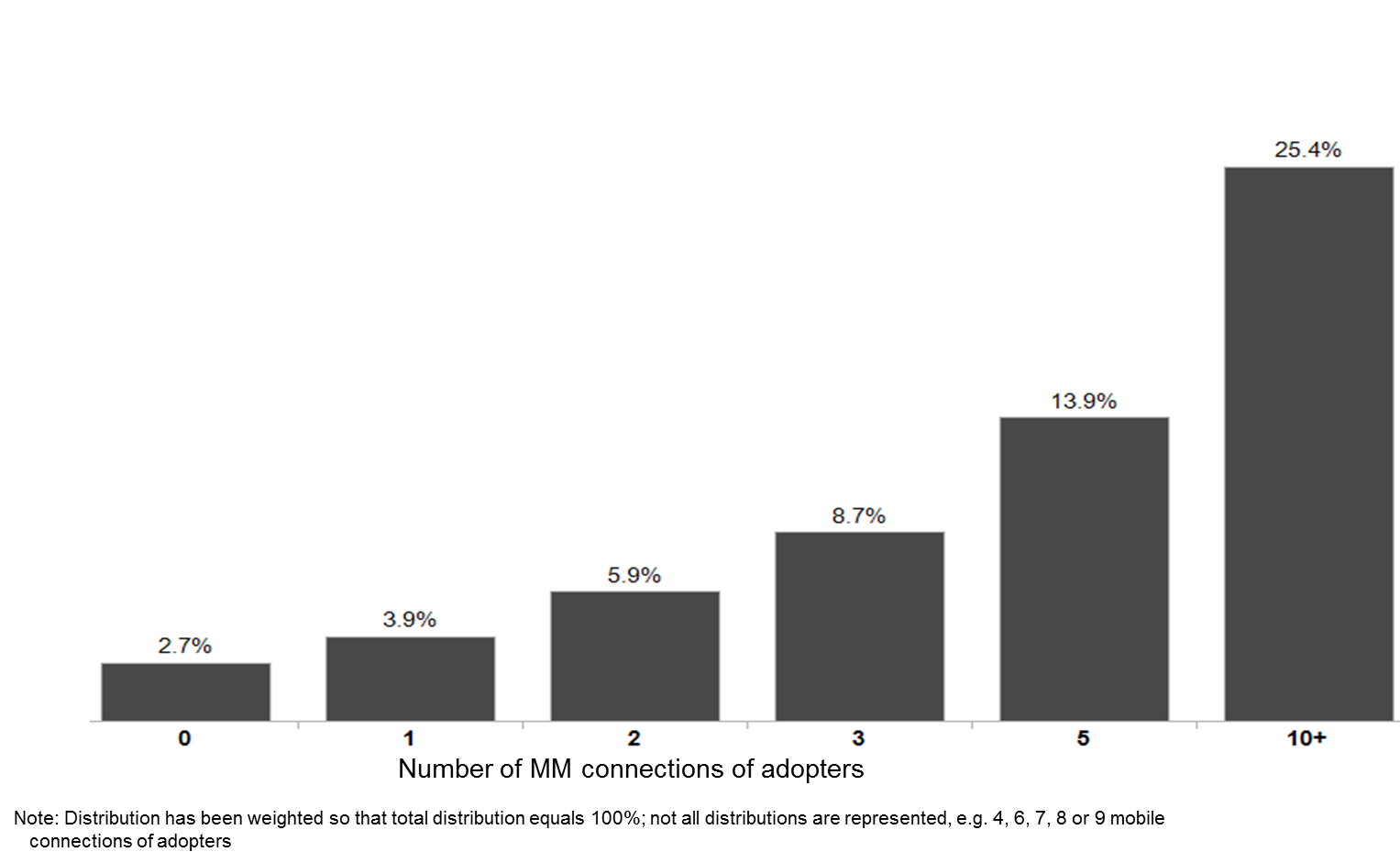
The first phase of the analysis revealed two key variables that indicate a higher propensity to adopt MM. The first variable is the social network and social interactions of the mobile user. That is, the number of MM users an individual is connected to (people whom the user connects to via phone or SMS). For instance, individuals with five MM connections are over 3.5 times more likely to adopt MM than individuals with only one MM connection, while individuals with two MM connections are more than twice as likely to adopt MM as individuals with no MM connections (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The relative probability of adoption increases with the number of MM connections
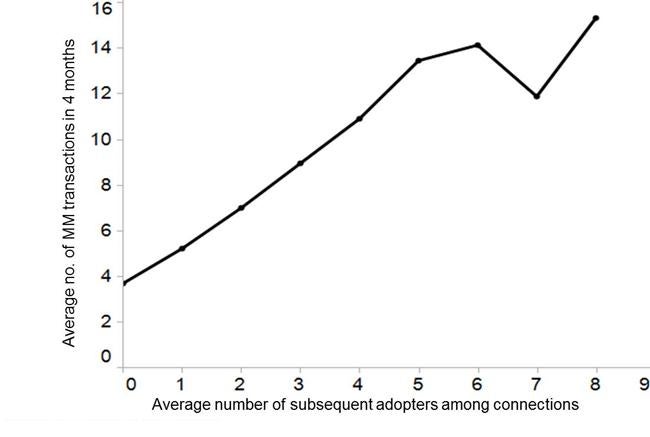
In addition, the more active MM users are, the more likely their non-MM connections are to adopt MM (Figure 2). For instance, active MM users who do twice as many transactions as other users are likely to have double the number of MM adopters among their connections.
Figure 2: MM virality is directly correlated with the level of activity
The second key variable is the user’s telecom usage profile (most notably, the quantity and variety of telecom products used—SMS, data, electronic top-ups, and voice). Adopters tend to call twice as much as nonadopters, send twice as many SMS, rely more on electronic recharges than scratch cards for airtime credit (albeit via agents), and use more data than nonadopters. In addition, technology leaders’ telecom expenditures are approximately three to four times higher than that of nonadopters.
These findings lead to several recommendations for MNOs wanting to drive MM adoption. First, analyze existing data to understand what drives adoption in your market. Second, identify those customers who are most likely to adopt MM and target them directly. Finally, identify and target those customers that are most likely to influence others to adopt.
These recommendations will be tested with campaigns in the pilot countries. For example, such campaigns might include offering customers with a higher probability of adopting a number of free MM transactions, or offering influential users value to send to non-users. The outcome of these campaigns will be described in an upcoming blog post.
------ The author Michel works in CGAP's Technology and Business Model Innovation team, where he leads work on branchless banking in South Africa.



Add new comment